- Constant Mesh Transmission Cars: A Comprehensive Guide
- What is a Constant Mesh Transmission?
- How Does a Constant Mesh Transmission Work? A CMT consists of the following components: * Input Shaft: Receives power from the engine and transfers it to the transmission. * Output Shaft: Transmits power to the wheels or further down the driveline. * Gear Cluster: Contains gears that are always in mesh with the gears on the input and output shafts. * Sliding Hubs: Move axially to engage different gear pairs on the gear cluster. * Synchronous Rings: Friction devices that synchronize the speed of the input shaft and the desired gear pair before engagement. When a gear change is initiated, the corresponding sliding hub moves to engage the appropriate gear pair. The synchronous rings help align the speeds of the input shaft and the target gear before engagement, ensuring smooth and efficient shifting. Types of Constant Mesh Transmissions CMTs can be classified into two main types: * Helical Gear CMT: Uses helical gears to reduce noise and improve durability. * Spur Gear CMT: Uses spur gears, which are simpler to manufacture but generate more noise. Advantages of Constant Mesh Transmissions CMTs offer several advantages over other transmission types: * Smooth Shifting: Gears are always in mesh, eliminating the need for gear alignment and reducing shift time. * Reduced Wear and Tear: Constant gear engagement distributes load over multiple teeth, extending their lifespan. * Improved Durability: Eliminating gear alignment issues and reducing wear extends the transmission’s overall life. * Quieter Operation: Helical gears, commonly used in CMTs, reduce noise levels compared to spur gears. * Increased Efficiency: Smooth gear changes minimize power loss and improve overall efficiency. Disadvantages of Constant Mesh Transmissions Despite their advantages, CMTs also have some drawbacks: * Complex Design: CMTs are more complex than other transmission types, which increases their manufacturing cost. * Weight and Size: CMTs tend to be heavier and larger than other types of transmissions due to the constant gear engagement mechanism. * Torque Capacity: CMTs generally have lower torque capacity compared to other transmission types. * Shift Speed: While CMTs provide smooth shifting, they may not be as quick as sequential or dual-clutch transmissions. Applications of Constant Mesh Transmissions CMTs are commonly used in various automotive applications, including: * Passenger Cars: CMTs offer a combination of smooth shifting and durability, making them suitable for everyday driving. * Trucks and Buses: CMTs can handle higher torque requirements and provide reliable performance in heavy-duty applications. * Off-Road Vehicles: CMTs excel in off-road environments where durability and gear engagement are crucial. * Industrial Machinery: CMTs are used in industrial machinery to provide precise gear changes and withstand harsh operating conditions. Maintenance and Troubleshooting Proper maintenance is essential for the longevity of constant mesh transmissions. Regular fluid changes, clutch adjustments, and component inspections are essential. Common problems associated with CMTs include: * Difficulty Shifting: Hard or grinding shifts can indicate worn or damaged synchronous rings or sliding hubs. * Noise: Excessive noise can be caused by worn gears or improper adjustment. * Oil Leaks: Seals and gaskets can deteriorate with age, leading to oil leaks that can cause damage if left unchecked. When experiencing any problems with a constant mesh transmission, it is recommended to seek professional assistance promptly to minimize damage and ensure proper repair. Conclusion Constant mesh transmissions offer the advantages of smooth shifting, reduced wear and tear, improved durability, and quiet operation. They are commonly used in various automotive and industrial applications. While they may be more complex and expensive than other transmission types, their reliability and smooth performance make them a preferred choice for many applications. By understanding the working principles, advantages, and disadvantages of constant mesh transmissions, technicians can better maintain and troubleshoot these critical components in vehicles and equipment.
- How Does a Constant Mesh Transmission Work?
- Types of Constant Mesh Transmissions CMTs can be classified into two main types: * Helical Gear CMT: Uses helical gears to reduce noise and improve durability. * Spur Gear CMT: Uses spur gears, which are simpler to manufacture but generate more noise. Advantages of Constant Mesh Transmissions CMTs offer several advantages over other transmission types: * Smooth Shifting: Gears are always in mesh, eliminating the need for gear alignment and reducing shift time. * Reduced Wear and Tear: Constant gear engagement distributes load over multiple teeth, extending their lifespan. * Improved Durability: Eliminating gear alignment issues and reducing wear extends the transmission’s overall life. * Quieter Operation: Helical gears, commonly used in CMTs, reduce noise levels compared to spur gears. * Increased Efficiency: Smooth gear changes minimize power loss and improve overall efficiency. Disadvantages of Constant Mesh Transmissions Despite their advantages, CMTs also have some drawbacks: * Complex Design: CMTs are more complex than other transmission types, which increases their manufacturing cost. * Weight and Size: CMTs tend to be heavier and larger than other types of transmissions due to the constant gear engagement mechanism. * Torque Capacity: CMTs generally have lower torque capacity compared to other transmission types. * Shift Speed: While CMTs provide smooth shifting, they may not be as quick as sequential or dual-clutch transmissions. Applications of Constant Mesh Transmissions CMTs are commonly used in various automotive applications, including: * Passenger Cars: CMTs offer a combination of smooth shifting and durability, making them suitable for everyday driving. * Trucks and Buses: CMTs can handle higher torque requirements and provide reliable performance in heavy-duty applications. * Off-Road Vehicles: CMTs excel in off-road environments where durability and gear engagement are crucial. * Industrial Machinery: CMTs are used in industrial machinery to provide precise gear changes and withstand harsh operating conditions. Maintenance and Troubleshooting Proper maintenance is essential for the longevity of constant mesh transmissions. Regular fluid changes, clutch adjustments, and component inspections are essential. Common problems associated with CMTs include: * Difficulty Shifting: Hard or grinding shifts can indicate worn or damaged synchronous rings or sliding hubs. * Noise: Excessive noise can be caused by worn gears or improper adjustment. * Oil Leaks: Seals and gaskets can deteriorate with age, leading to oil leaks that can cause damage if left unchecked. When experiencing any problems with a constant mesh transmission, it is recommended to seek professional assistance promptly to minimize damage and ensure proper repair. Conclusion Constant mesh transmissions offer the advantages of smooth shifting, reduced wear and tear, improved durability, and quiet operation. They are commonly used in various automotive and industrial applications. While they may be more complex and expensive than other transmission types, their reliability and smooth performance make them a preferred choice for many applications. By understanding the working principles, advantages, and disadvantages of constant mesh transmissions, technicians can better maintain and troubleshoot these critical components in vehicles and equipment.
- Types of Constant Mesh Transmissions
- Advantages of Constant Mesh Transmissions CMTs offer several advantages over other transmission types: * Smooth Shifting: Gears are always in mesh, eliminating the need for gear alignment and reducing shift time. * Reduced Wear and Tear: Constant gear engagement distributes load over multiple teeth, extending their lifespan. * Improved Durability: Eliminating gear alignment issues and reducing wear extends the transmission’s overall life. * Quieter Operation: Helical gears, commonly used in CMTs, reduce noise levels compared to spur gears. * Increased Efficiency: Smooth gear changes minimize power loss and improve overall efficiency. Disadvantages of Constant Mesh Transmissions Despite their advantages, CMTs also have some drawbacks: * Complex Design: CMTs are more complex than other transmission types, which increases their manufacturing cost. * Weight and Size: CMTs tend to be heavier and larger than other types of transmissions due to the constant gear engagement mechanism. * Torque Capacity: CMTs generally have lower torque capacity compared to other transmission types. * Shift Speed: While CMTs provide smooth shifting, they may not be as quick as sequential or dual-clutch transmissions. Applications of Constant Mesh Transmissions CMTs are commonly used in various automotive applications, including: * Passenger Cars: CMTs offer a combination of smooth shifting and durability, making them suitable for everyday driving. * Trucks and Buses: CMTs can handle higher torque requirements and provide reliable performance in heavy-duty applications. * Off-Road Vehicles: CMTs excel in off-road environments where durability and gear engagement are crucial. * Industrial Machinery: CMTs are used in industrial machinery to provide precise gear changes and withstand harsh operating conditions. Maintenance and Troubleshooting Proper maintenance is essential for the longevity of constant mesh transmissions. Regular fluid changes, clutch adjustments, and component inspections are essential. Common problems associated with CMTs include: * Difficulty Shifting: Hard or grinding shifts can indicate worn or damaged synchronous rings or sliding hubs. * Noise: Excessive noise can be caused by worn gears or improper adjustment. * Oil Leaks: Seals and gaskets can deteriorate with age, leading to oil leaks that can cause damage if left unchecked. When experiencing any problems with a constant mesh transmission, it is recommended to seek professional assistance promptly to minimize damage and ensure proper repair. Conclusion Constant mesh transmissions offer the advantages of smooth shifting, reduced wear and tear, improved durability, and quiet operation. They are commonly used in various automotive and industrial applications. While they may be more complex and expensive than other transmission types, their reliability and smooth performance make them a preferred choice for many applications. By understanding the working principles, advantages, and disadvantages of constant mesh transmissions, technicians can better maintain and troubleshoot these critical components in vehicles and equipment.
- Advantages of Constant Mesh Transmissions
- Disadvantages of Constant Mesh Transmissions Despite their advantages, CMTs also have some drawbacks: * Complex Design: CMTs are more complex than other transmission types, which increases their manufacturing cost. * Weight and Size: CMTs tend to be heavier and larger than other types of transmissions due to the constant gear engagement mechanism. * Torque Capacity: CMTs generally have lower torque capacity compared to other transmission types. * Shift Speed: While CMTs provide smooth shifting, they may not be as quick as sequential or dual-clutch transmissions. Applications of Constant Mesh Transmissions CMTs are commonly used in various automotive applications, including: * Passenger Cars: CMTs offer a combination of smooth shifting and durability, making them suitable for everyday driving. * Trucks and Buses: CMTs can handle higher torque requirements and provide reliable performance in heavy-duty applications. * Off-Road Vehicles: CMTs excel in off-road environments where durability and gear engagement are crucial. * Industrial Machinery: CMTs are used in industrial machinery to provide precise gear changes and withstand harsh operating conditions. Maintenance and Troubleshooting Proper maintenance is essential for the longevity of constant mesh transmissions. Regular fluid changes, clutch adjustments, and component inspections are essential. Common problems associated with CMTs include: * Difficulty Shifting: Hard or grinding shifts can indicate worn or damaged synchronous rings or sliding hubs. * Noise: Excessive noise can be caused by worn gears or improper adjustment. * Oil Leaks: Seals and gaskets can deteriorate with age, leading to oil leaks that can cause damage if left unchecked. When experiencing any problems with a constant mesh transmission, it is recommended to seek professional assistance promptly to minimize damage and ensure proper repair. Conclusion Constant mesh transmissions offer the advantages of smooth shifting, reduced wear and tear, improved durability, and quiet operation. They are commonly used in various automotive and industrial applications. While they may be more complex and expensive than other transmission types, their reliability and smooth performance make them a preferred choice for many applications. By understanding the working principles, advantages, and disadvantages of constant mesh transmissions, technicians can better maintain and troubleshoot these critical components in vehicles and equipment.
- Disadvantages of Constant Mesh Transmissions
- Applications of Constant Mesh Transmissions CMTs are commonly used in various automotive applications, including: * Passenger Cars: CMTs offer a combination of smooth shifting and durability, making them suitable for everyday driving. * Trucks and Buses: CMTs can handle higher torque requirements and provide reliable performance in heavy-duty applications. * Off-Road Vehicles: CMTs excel in off-road environments where durability and gear engagement are crucial. * Industrial Machinery: CMTs are used in industrial machinery to provide precise gear changes and withstand harsh operating conditions. Maintenance and Troubleshooting Proper maintenance is essential for the longevity of constant mesh transmissions. Regular fluid changes, clutch adjustments, and component inspections are essential. Common problems associated with CMTs include: * Difficulty Shifting: Hard or grinding shifts can indicate worn or damaged synchronous rings or sliding hubs. * Noise: Excessive noise can be caused by worn gears or improper adjustment. * Oil Leaks: Seals and gaskets can deteriorate with age, leading to oil leaks that can cause damage if left unchecked. When experiencing any problems with a constant mesh transmission, it is recommended to seek professional assistance promptly to minimize damage and ensure proper repair. Conclusion Constant mesh transmissions offer the advantages of smooth shifting, reduced wear and tear, improved durability, and quiet operation. They are commonly used in various automotive and industrial applications. While they may be more complex and expensive than other transmission types, their reliability and smooth performance make them a preferred choice for many applications. By understanding the working principles, advantages, and disadvantages of constant mesh transmissions, technicians can better maintain and troubleshoot these critical components in vehicles and equipment.
- Applications of Constant Mesh Transmissions
- Maintenance and Troubleshooting Proper maintenance is essential for the longevity of constant mesh transmissions. Regular fluid changes, clutch adjustments, and component inspections are essential. Common problems associated with CMTs include: * Difficulty Shifting: Hard or grinding shifts can indicate worn or damaged synchronous rings or sliding hubs. * Noise: Excessive noise can be caused by worn gears or improper adjustment. * Oil Leaks: Seals and gaskets can deteriorate with age, leading to oil leaks that can cause damage if left unchecked. When experiencing any problems with a constant mesh transmission, it is recommended to seek professional assistance promptly to minimize damage and ensure proper repair. Conclusion Constant mesh transmissions offer the advantages of smooth shifting, reduced wear and tear, improved durability, and quiet operation. They are commonly used in various automotive and industrial applications. While they may be more complex and expensive than other transmission types, their reliability and smooth performance make them a preferred choice for many applications. By understanding the working principles, advantages, and disadvantages of constant mesh transmissions, technicians can better maintain and troubleshoot these critical components in vehicles and equipment.
- Maintenance and Troubleshooting
- Conclusion
Constant Mesh Transmission Cars: A Comprehensive Guide
What is a Constant Mesh Transmission?
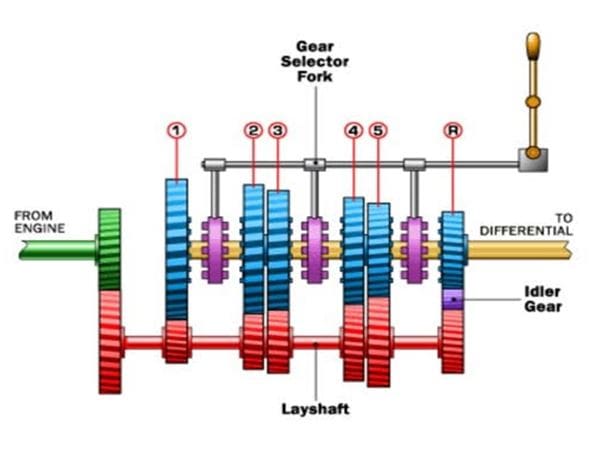
In a constant mesh transmission (CMT), gears are in constant engagement, allowing for seamless gear changes. Unlike manual transmissions where gears are shifted into and out of alignment, a CMT maintains contact between all gear pairs. This results in smoother shifting, reduced wear and tear, and improved durability.
How Does a Constant Mesh Transmission Work?
A CMT consists of the following components:
* Input Shaft: Receives power from the engine and transfers it to the transmission.
* Output Shaft: Transmits power to the wheels or further down the driveline.
* Gear Cluster: Contains gears that are always in mesh with the gears on the input and output shafts.
* Sliding Hubs: Move axially to engage different gear pairs on the gear cluster.
* Synchronous Rings: Friction devices that synchronize the speed of the input shaft and the desired gear pair before engagement.
When a gear change is initiated, the corresponding sliding hub moves to engage the appropriate gear pair. The synchronous rings help align the speeds of the input shaft and the target gear before engagement, ensuring smooth and efficient shifting.
Types of Constant Mesh Transmissions
CMTs can be classified into two main types:
* Helical Gear CMT: Uses helical gears to reduce noise and improve durability.
* Spur Gear CMT: Uses spur gears, which are simpler to manufacture but generate more noise.
Advantages of Constant Mesh Transmissions
CMTs offer several advantages over other transmission types:
* Smooth Shifting: Gears are always in mesh, eliminating the need for gear alignment and reducing shift time.
* Reduced Wear and Tear: Constant gear engagement distributes load over multiple teeth, extending their lifespan.
* Improved Durability: Eliminating gear alignment issues and reducing wear extends the transmission’s overall life.
* Quieter Operation: Helical gears, commonly used in CMTs, reduce noise levels compared to spur gears.
* Increased Efficiency: Smooth gear changes minimize power loss and improve overall efficiency.
Disadvantages of Constant Mesh Transmissions
Despite their advantages, CMTs also have some drawbacks:
* Complex Design: CMTs are more complex than other transmission types, which increases their manufacturing cost.
* Weight and Size: CMTs tend to be heavier and larger than other types of transmissions due to the constant gear engagement mechanism.
* Torque Capacity: CMTs generally have lower torque capacity compared to other transmission types.
* Shift Speed: While CMTs provide smooth shifting, they may not be as quick as sequential or dual-clutch transmissions.
Applications of Constant Mesh Transmissions
CMTs are commonly used in various automotive applications, including:
* Passenger Cars: CMTs offer a combination of smooth shifting and durability, making them suitable for everyday driving.
* Trucks and Buses: CMTs can handle higher torque requirements and provide reliable performance in heavy-duty applications.
* Off-Road Vehicles: CMTs excel in off-road environments where durability and gear engagement are crucial.
* Industrial Machinery: CMTs are used in industrial machinery to provide precise gear changes and withstand harsh operating conditions.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Proper maintenance is essential for the longevity of constant mesh transmissions. Regular fluid changes, clutch adjustments, and component inspections are essential.
Common problems associated with CMTs include:
* Difficulty Shifting: Hard or grinding shifts can indicate worn or damaged synchronous rings or sliding hubs.
* Noise: Excessive noise can be caused by worn gears or improper adjustment.
* Oil Leaks: Seals and gaskets can deteriorate with age, leading to oil leaks that can cause damage if left unchecked.
When experiencing any problems with a constant mesh transmission, it is recommended to seek professional assistance promptly to minimize damage and ensure proper repair.
Conclusion
Constant mesh transmissions offer the advantages of smooth shifting, reduced wear and tear, improved durability, and quiet operation. They are commonly used in various automotive and industrial applications. While they may be more complex and expensive than other transmission types, their reliability and smooth performance make them a preferred choice for many applications. By understanding the working principles, advantages, and disadvantages of constant mesh transmissions, technicians can better maintain and troubleshoot these critical components in vehicles and equipment.